This blog post is written and published on AzureStack.blog: https://azurestack.blog/2016/02/adding-and-using-the-dsc-for-linux-vm-extension-to-azure-stack-tp1/
In my previous post I described how to add a CentOS image to Azure Stack so tenants can deploy Linux machines. Now that we have an image available, it’s time for the next step. Deploy a Linux VM and have DSC configure it!
Acquire the DSC For Linux VM Extension
VM Extensions are handled by the CRP which offers up the extensions located in the C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Share\CRP\GuestArtifactRepository directory.
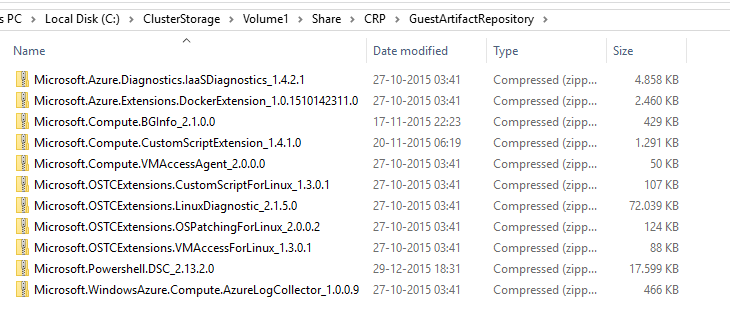
If you look closely, you probably notice that the DSC For Linux VM extension is not present. It did not ship with Azure Stack TP1. So how to make it available? The extension is available on GitHub but to spare you the trouble I had, don’t download it here. I got it to work but once the VM was installing the extension, thing started to break down and unknown errors were thrown.
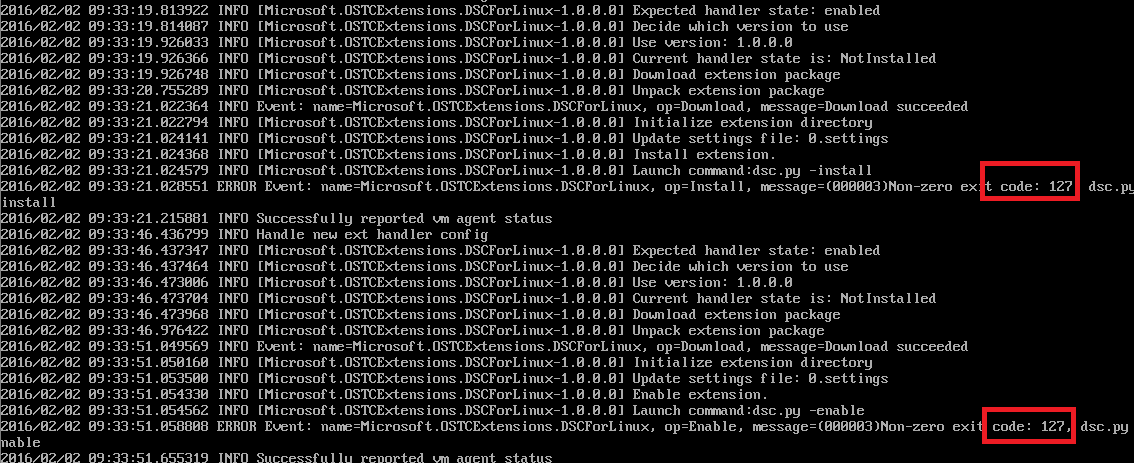
When investigating the issue, I noticed the extension was present on the VM in zipped up form. I figured I would deploy a VM in Azure and see if I could acquire the extension that way. Bingo! To safe you the trouble from doing the same, I’ve put the extension on my GitHub for you to download. I did not notice any obvious differences between the version used in Azure and the one I got from the Azure GitHub repo but the end result is that the one I got from Azure worked.
Once downloaded from my GitHub you need to make the extension available for the CRP by placing the file in zipped up form at C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Share\CRP\GuestArtifactRepository. Make sure to unblock it!
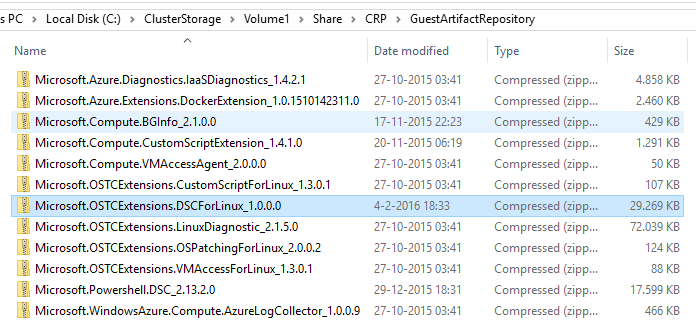
You could also run this script to have it done in one go:
$Download = @{
Uri = 'https://github.com/bgelens/BlogItems/raw/master/Microsoft.OSTCExtensions.DSCForLinux_1.0.0.0.zip'
OutFile = 'C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Share\CRP\GuestArtifactRepository\Microsoft.OSTCExtensions.DSCForLinux_1.0.0.0.zip'
UseBasicParsing = $true
}
Invoke-WebRequest @Download
Unblock-File -Path 'C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Share\CRP\GuestArtifactRepository\Microsoft.OSTCExtensions.DSCForLinux_1.0.0.0.zip'
The extension is now available.
Prepping a configuration
Because PowerShell does not run on Linux, the DSC For Linux extension is not able to compile PowerShell DSC Configuration scripts into MOF files. Instead you need to use the DSC For Linux extension with pre-compiled MOF or meta.MOF files.
First let’s create a configuration script and compile a MOF file from it. All following actions take place on the client VM.
#region get the Linux DSC Resource module
Install-Module -Name NX -Scope AllUsers -Force
#endregion
#region Linux Configuration
Configuration NginX {
param (
[String] $HTMLData = '<center><H1>Hello World!</H1></center>'
)
Import-DSCResource -Module NX
nxPackage EPEL {
Ensure = 'Present'
Name = 'epel-release'
PackageManager = 'Yum'
}
nxPackage NginX {
Ensure = 'Present'
Name = 'nginx'
PackageManager = 'Yum'
DependsOn = '[nxPackage]EPEL'
}
nxFile MyCoolWebPage {
DestinationPath = '/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html'
Contents = $HTMLData
Force = $true
DependsOn = '[nxPackage]NginX'
}
nxService NginXService {
Name = 'nginx'
Controller = 'systemd'
Enabled = $true
State = 'Running'
DependsOn = '[nxFile]MyCoolWebPage'
}
}
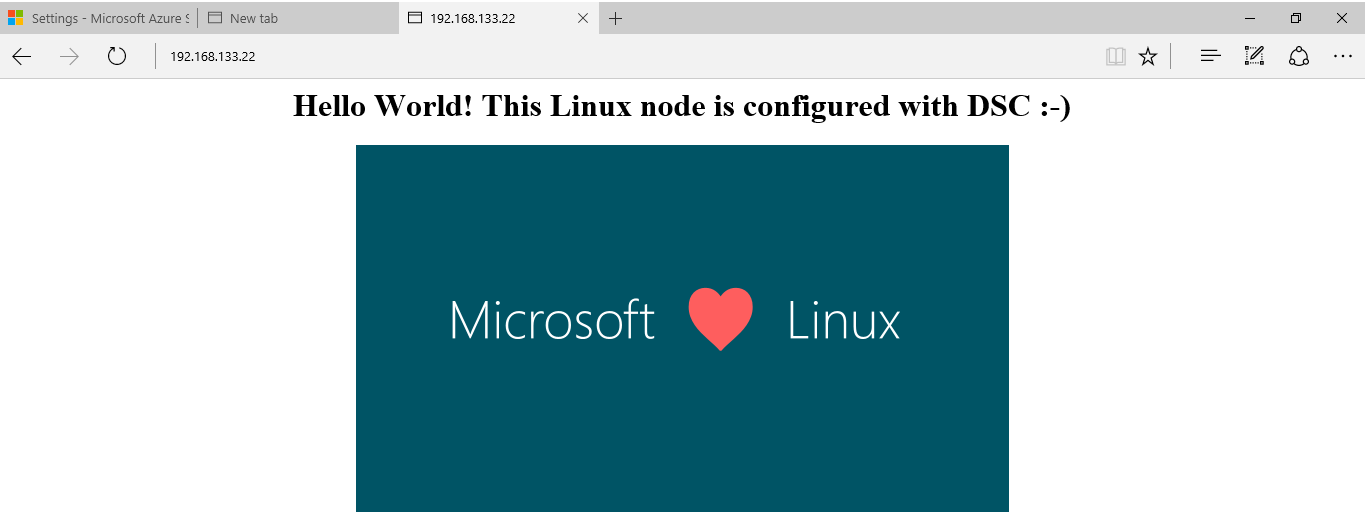
$WebSite = '<center><H1>Hello World! This Linux node is configured with DSC :-)</H1></center>
<center><img src="https://msdnshared.blob.core.windows.net/media/TNBlogsFS/prod.evol.blogs.technet.com/CommunityServer.Blogs.Components.WeblogFiles/00/00/00/41/57/ms_loves_linux.png"></center>'
NginX -HTMLData $WebSite -OutputPath c:\NginX
#endregion
This script will download the NX DSC Resource Module first so PowerShell will be able to compile the MOF. Next, a configuration is loaded which will make the Linux box into a webserver. Finally, the configuration is called and compiled by PowerShell. The simple HTML code declared in the WebSite variable will be passed to the configuration parameter. The resulting MOF can be found at to C:\NginX\localhost.mof.
Now we have a configuration for a Linux box we need to make sure that the DSC For Linux Extension can get to it when the VM gets deployed. To do this, I’ll create a Storage Account to contain the MOF file so the extension can download it from there. The extension can deal with storage accounts natively but for this demo I simulate the MOF file to be located on a publicly available Uri. When running the script you should modify the TenantUser variable on line 2.
#region add AzureStack environment
$TenantUser = 'AzureStackUser@bgelens.nl'
$Cred = Get-Credential -UserName $TenantUser -Message "Provide your creds"
#Construct Uri parameter value for Invoke-WebRequest
$TenantParam = @{
Uri = 'https://login.windows.net/{0}/.well-known/openid-configuration' -f $TenantUser.Split('@')[1]
}
$TenantData = Invoke-WebRequest @TenantParam | ConvertFrom-Json
#Get Tenant Id
$TenantId = $TenantData.userinfo_endpoint.Split('/')[3]
#Construct parameters for Add-AzureRmEnvironmnet
$ASEnvParam = @{
Name = 'Azure Stack'
ActiveDirectoryEndpoint = "https://login.windows.net/$TenantId/"
ActiveDirectoryServiceEndpointResourceId = 'https://azurestack.local-api/'
ResourceManagerEndpoint = 'https://api.azurestack.local/'
GalleryEndpoint = 'https://gallery.azurestack.local/'
GraphEndpoint = 'https://graph.windows.net/'
}
#Add AzureStack Environement
$ASEnv = Add-AzureRmEnvironment @ASEnvParam
$ASProfile = Add-AzureRmAccount -Environment $ASEnv -Credential $Cred
Select-AzureRmProfile -Profile $ASProfile
Get-AzureRmSubscription | Select-AzureRmSubscription
#endregion
#region create storage account, upload MOF file and return Uri
$RG = New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name 'LinuxDSC' -Location 'Local'
$StorageAcct = $RG | New-AzureRmStorageAccount -Name 'linuxdsc' -Type Standard_LRS
$StorageContainer = New-AzureStorageContainer -Context $StorageAcct.Context -Name 'mof' -Permission Blob
$UpLoad = $StorageContainer | Set-AzureStorageBlobContent -File C:\NginX\localhost.mof -Context $StorageAcct.Context
$MOFUri = $UpLoad.ICloudBlob.Uri.AbsoluteUri
$MOFUri
#endregion
The script will figure out the Tenant Id based on the domain name used to authenticate. Then it will add Azure Stack as an environment for PowerShell cmdlets to use. It will authenticate and while doing so, it will select the Azure Stack environment just added as the context. Finally, a storage account is created containing an anonymously accessible container. The mof file compiled earlier will be uploaded to the container and the Uri on which it is available will be printed out (copy this as we need it later, https://linuxdsc.blob.azurestack.local/mof/localhost.mof).
Using the DSC For Linux VM Extension
Now everything is in place we can provision a VM and use the DSC For Linux extension with it to finalize the VMs configuration during creation. The easiest way is to do this is through a JSON template as the VM extension needs name resolution for the extension to work properly (in current TP1 we need to explicitly configure DNS).
Copy the following template and save it on the ClientVM on the root of C:. Name it DeployVMWithDSCForLinux.json. If you followed my blogpost on adding CentOS to Azure Stack and changed the publisher name for example, you need to adjust this template accordingly!
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"username": {
"type": "string",
"metadata": {
"description": "Username for the Virtual Machine."
}
},
"password": {
"type": "securestring",
"metadata": {
"description": "Password for the Virtual Machine."
}
},
"vmName": {
"type": "string",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of the vm, will be used as DNS Name for the Public IP used to access the Virtual Machine."
}
},
"vmSize": {
"type": "string",
"metadata": {
"description": "VM size"
},
"defaultValue": "Standard_A2"
},
"mode": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "Push",
"metadata": {
"description": "The functional mode, push MOF configuration (Push), distribute MOF configuration (Pull)"
},
"allowedValues": [
"Push",
"Pull"
]
},
"MofFileUri": {
"type": "string",
"metadata": {
"description" : "The Uri of the MOF or meta.MOF file"
}
}
},
"variables": {
"api-version": "2015-05-01-preview",
"computeapi-version": "2015-06-15",
"virtualNetworkName": "vnet-dsc",
"nicName": "[parameters('vmName')]",
"publicIPAddressName": "[parameters('vmName')]",
"vnetAddressPrefix": "10.0.0.0/16",
"subnetName": "dsc",
"subnetPrefix": "10.0.0.0/24",
"publicIPAddressType": "Dynamic",
"vnetID": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks',variables('virtualNetworkName'))]",
"subnetRef": "[concat(variables('vnetID'),'/subnets/',variables('subnetName'))]",
"vmStorageAccountContainerName": "vhds",
"storageAccountType": "Standard_LRS",
"imagePublisher": "BGelens",
"imageOffer": "CentOS",
"sku": "7.2",
"OSDiskName": "osdiskfordsc",
"networkSecurityGroupName": "[parameters('vmName')]",
"location": "local",
"newStorageAccountName": "[toLower(parameters('vmName'))]"
},
"resources": [
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('api-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts",
"name": "[variables('newStorageAccountName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"properties": {
"accountType": "[variables('storageAccountType')]"
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('api-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups",
"name": "[variables('networkSecurityGroupName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"tags": {
"displayName": "NetworkSecurityGroup"
},
"properties": {
"securityRules": [
{
"name": "http",
"properties": {
"protocol": "Tcp",
"sourcePortRange": "*",
"destinationPortRange": "80",
"sourceAddressPrefix": "*",
"destinationAddressPrefix": "*",
"access": "Allow",
"priority": 200,
"direction": "Inbound",
"description": "NginX inbound"
}
},
{
"name": "ssh",
"properties": {
"protocol": "Tcp",
"sourcePortRange": "*",
"destinationPortRange": "22",
"sourceAddressPrefix": "*",
"destinationAddressPrefix": "*",
"access": "Allow",
"priority": 100,
"direction": "Inbound",
"description": "SSH inbound"
}
}
]
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('api-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses",
"name": "[variables('publicIPAddressName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"properties": {
"publicIPAllocationMethod": "[variables('publicIPAddressType')]"
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('api-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks",
"name": "[variables('virtualNetworkName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/', variables('networkSecurityGroupName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"addressSpace": {
"addressPrefixes": [
"[variables('vnetAddressPrefix')]"
]
},
"subnets": [
{
"name": "[variables('subnetName')]",
"properties": {
"addressPrefix": "[variables('subnetPrefix')]",
"networkSecurityGroup": {
"id": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups', variables('networkSecurityGroupName'))]"
}
}
}
],
"dhcpOptions": {
"dnsServers": [ "192.168.100.2" ]
}
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('api-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces",
"name": "[variables('nicName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/', variables('publicIPAddressName'))]",
"[concat('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/', variables('virtualNetworkName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"dnsSettings": {
"dnsServers": [ "192.168.100.2" ]
},
"ipConfigurations": [
{
"name": "ipconfig1",
"properties": {
"privateIPAllocationMethod": "Dynamic",
"publicIPAddress": {
"id": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses',variables('publicIPAddressName'))]"
},
"subnet": {
"id": "[variables('subnetRef')]"
}
}
}
]
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('computeapi-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines",
"name": "[parameters('vmName')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/', variables('newStorageAccountName'))]",
"[concat('Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/', variables('nicName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"hardwareProfile": {
"vmSize": "[parameters('vmSize')]"
},
"osProfile": {
"computerName": "[parameters('vmName')]",
"adminUsername": "[parameters('username')]",
"adminPassword": "[parameters('password')]"
},
"storageProfile": {
"imageReference": {
"publisher": "[variables('imagePublisher')]",
"offer": "[variables('imageOffer')]",
"sku": "[variables('sku')]",
"version": "latest"
},
"osDisk": {
"name": "osdisk1",
"vhd": {
"uri": "[concat('http://',variables('newStorageAccountName'),'.blob.azurestack.local/',variables('vmStorageAccountContainerName'),'/',variables('OSDiskName'),'.vhd')]"
},
"caching": "ReadWrite",
"createOption": "FromImage"
}
},
"networkProfile": {
"networkInterfaces": [
{
"id": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces',variables('nicName'))]"
}
]
}
}
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('computeapi-version')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions",
"name": "[concat(parameters('vmName'),'/enabledsc')]",
"location": "[variables('location')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/', parameters('vmName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.OSTCExtensions",
"type": "DSCForLinux",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.0",
"settings": {
"Mode": "[parameters('mode')]",
"MofFileUri": "[parameters('MofFileUri')]"
}
}
}
],
"outputs": {
"Uri": {
"type": "string",
"value": "[concat('http://',reference(resourceId('Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses',variables('publicIPAddressName')),providers('Microsoft.Network', 'publicIPAddresses').apiVersions[0]).ipAddress)]"
}
}
}
Next, run the following script from the PowerShell session you used earlier. If you close it, please run the region “add AzureStack environment” again. You should change the MofFileUri if you modified the previous script and you could of course assign your own username and password!
$DeployRG = New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name DSCForLinux -Location Local
$DeployParams = @{
TemplateFile = 'C:\DeployVMWithDSCForLinux.json'
TemplateParameterObject = @{
username = 'ben'
password = 'Welkom01'
vmName = 'DSCForLinux01'
mode = 'Push'
MofFileUri = 'https://linuxdsc.blob.azurestack.local/mof/localhost.mof'
}
Mode = 'Complete'
Force = $true
}
$DeployRG | New-AzureRmResourceGroupDeployment @DeployParams
Once the template is deployed you should see similar output as the following:
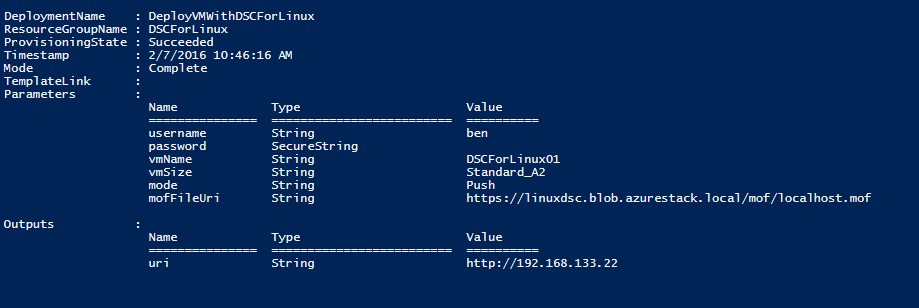
When you navigate to the uri stated in the Outputs you should see the WebPage hosted by NginX!
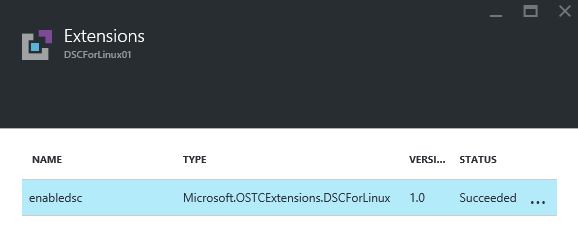
When navigating to the VM extensions via the portal, you should see the extension status as succeeded as well.
Alternatively from a JSON template. You could also use PowerShell to add the extension to an already existing VM. This would look something like this:
$VM = get-azurermvm -Name testdscextlinux -ResourceGroupName testdscextlinux
#$extension = Get-AzureRmVMExtensionImage -Location local -PublisherName Microsoft.OSTCExtensions -Type DSCForLinux
Set-AzureRmVMExtension -Publisher Microsoft.OSTCExtensions `
-ExtensionType DSCForLinux `
-TypeHandlerVersion "1.0" `
-Settings @{mode='push'; MofFileUri = 'https://dscstorage.blob.azurestack.local/dscconfig/localhost.mof'} `
-VMName $vm.Name `
-ResourceGroupName $vm.ResourceGroupName `
-Name 'DSCForLinux' `
-Location $vm.Location
Note that Get-AzureRmVMExtensionImage currently does not work against Azure Stack so it could be a little bit tough to figure out all the data you need to specify.
Alternatively from a PowerShell invoked deployment, you could also copy paste the template content into the Template Deployment widget and go from there.
Hope you enjoyed reading !
