This blog post is written and published on Hyper-V.nu: https://hyper-v.nu/archives/bgelens/2014/08/bare-metal-post-deployment-pre-conditions-part-2/
This blog post series consists of 5 parts:
- Part 1: Introduction and Scenario
- Part 2: Pre-Conditions (this blog post)
- Part 3: Constructing the Post-Deployment automation
- Part 4: Constructing the Post-Deployment automation continued
- Part 5: Running the Post-Deployment automation and Bonus
Pre-Conditions
In this blog post all fundamentals will be put into place so we have some hooks and workable items for the automation to utilize.
I’ll assume you have a working SCVMM and SMA environment and are already able to perform the bare metal deployment process itself. For an excellent guide on how to start with SMA, download the SMA Whitepaper written by MVP Michael Rueefli. I also assume Windows Azure Pack is in place to front-end SMA.
You have to install the SCVMM Console on the SMA Runbook Worker for the described runbooks to work.
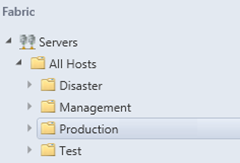
Host Groups
Because one server model can of course be utilized for multiple environments (e.g. Production and Test), I have configured multiple hosts groups for these servers. The host groups are used as a filter mechanism for the SMA runbooks to apply different configurations, if any exist (e.g. uplink port profile or differences in hardware resources).
Hyper-V Host Custom Property
To determine which Hyper-V hosts are subject to a post deployment process, a Custom Property is implemented and bound to the Hyper-V host object. In this case we define that if this property on a host has no value, the post deployment process will run against that.
To create a custom property in SCVMM, run the following cmdlet:
New-SCCustomProperty -Name "Post Deployment Status" -AddMember VMHost
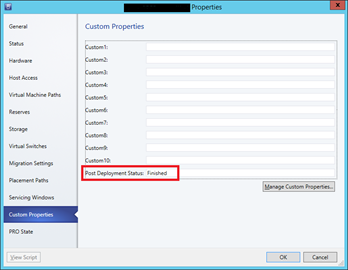
This host has finished its post deployment process and won’t be part of the next cycle.
Custom Resource
Post-deployment tasks are run through a series of scripts, coordinated by an SMA runbook, which are executed on the Hyper-V hosts. SCVMM will be used to deploy and start the scripts. The scripts and supporting utilities are stored in an SCVMM custom resource. To create a custom resource simply create a new folder in your SCVMM library and name it with a “.cr” extension (e.g. Hostdeploy.cr), then refresh your library.
HPSUM Share
During post deployment, HP Smart Update Manager (HPSUM) will be invoked to install drivers and additional HP software. HPSUM and packages must be present on a file server share (a later described custom resource script will invoke HPSUM). Download the latest (Service Pack for ProLiant) (SPP) and extract the content of the swpackages folder to the share.
During the post-deployment process, the content of the share is copied to the Hyper-V host entirely so HPSUM can be executed with a local repository (earlier versions ran well with a repository on a share, the newer versions unfortunately do not). You can remove the Virtual connect firmware from the HPSUM share, this will reduce the amount of data which need to be copied dramatically.
Download the latest version of “OneCommand Fibre Channel and Converged Network Adapter Configuration Utility” from the hp.com website and add the CP package to the HPSUM share. This utility will be used by “BL460_npiv.ps1” (custom resource script) to enable NPIV support.
SMA Variables and Stored Credentials
For SMA to interface with other components, some variables and credentials need to be created as an SMA Asset.
| Asset Name | Asset Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SMA SCVMM Service Account | Credential | Domain Account. Member of SCVMM Administrator Role |
| VMMServer | String Variable | FQDN of VMM Server |
| SMAWebServer | String Variable | FQDN of SMA Web Administration Server |
The SMA Runbook worker account must be an SMA Administrator to start child runbooks via the SMA web service. This can be done either by making the service account a member of the Active Directory group specified during installation or as a member of the smaAdminGroup local group on the SMA web server. You can of course also create a credential asset and adjust the runbook to use these credentials when starting the child runbook which would probably be better.
SCVMM Stored Credentials
For SCVMM to run scripts on Hyper-V hosts, an SCVMM Run As account with local administrator rights on the Hyper-V hosts needs to be in place.
| Run As Account Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| SCVMM Admin Run As Account | Domain Account. |
Member of Local Administrators Group on Hyper-V hosts.
Rename Uplink Port Profile Sets
When you configure a Logical Switch with an uplink port, an uplink port profile set is created. The name is based on the uplink port profile display name appended by a GUID. Since we need to specify the uplink port profile set to use when we implement the logical switch on the Hyper-V host, and the GUID will complicate this a little bit, we will strip the GUID off. This is not a mandatory pre-condition but helpful for this blog.
To do this for all uplink sets run:
Get-SCUplinkPortProfileSet |%{$_ | Set-SCUplinkPortProfileSet -Name $_.DisplayName}
To do this for all uplink sets associated with a logical switch run:
[string]$switchname = "infra"
Get-SCUplinkPortProfileSet -LogicalSwitch (Get-SCLogicalSwitch -Name $switchname) |%{$_ | Set-SCUplinkPortProfileSet -Name $_.DisplayName}
