Some time ago I contributed 3 new Terraform resources to the AzureRM Resource Provider:
- azurerm_automation_module
- azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration
- azurerm_automation_dsc_nodeconfiguration
This was my first ever contribution to a Go project so I’m very proud this got merged!
These 3 resources where the missing pin (for me at least) to have an end-2-end scenario enabled where pre-compiled DSC mof files and DSC resource modules could be send to an Azure Automation Account. This enables Terraform VM deployments including Guest state configuration assignment handled through Azure Automation.
In this blog post I’ll demonstrate the use of these resources. I won’t go into detail on how to get started with Terraform and such as there is plenty of info available already.
I’m using Terraform 0.11.11 and I have added it to my path so it’s available from any folder I’m in. I’m using the azurerm provider version 1.21.
I’ve defined and applied a starter Terraform file and I’ll work from there. I’m using an SPN for authentication and have added the variable values to my environmental variables before I ran this.
variable "ARM_CLIENT_ID" {}
variable "ARM_CLIENT_SECRET" {}
variable "ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID" {}
variable "ARM_TENANT_ID" {}
provider "azurerm" {
version = "1.21"
client_id = "${var.ARM_CLIENT_ID}"
client_secret = "${var.ARM_CLIENT_SECRET}"
subscription_id = "${var.ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}"
tenant_id = "${var.ARM_TENANT_ID}"
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "aadscrg" {
name = "aadscrg"
location = "westeurope"
}
resource "azurerm_automation_account" "aa" {
name = "aadsc01"
location = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
sku {
name = "Basic"
}
}
For this blog post I’m keeping things simple as I’m just illustrating the use of the Terraform resources. We’ll be using the following DSC configuration:
configuration timezone {
Import-DscResource -ModuleName ComputerManagementDsc -ModuleVersion 6.1.0.0
TimeZone westeustandard {
IsSingleInstance = 'Yes'
TimeZone = 'W. Europe Standard Time'
}
}
So we know we need ComputerManagementDsc DSC Resource module with version 6.1.0.0 to be available in Azure Automation as a Module asset so that LCMs can download this module when they don’t have it already. To do this we need to add the Terraform AzureRM resource azurerm_automation_module to our Terraform file.
The resource needs a download link where the zip or nupkg is available. You could of course publish a module to an Azure Storage Account and pass the link to the blob to this resource but in this case, the Module is available on the PowerShell Gallery. We only need to find the download link for it. So let’s find the download link for ComputerManagementDsc Resource Module of verion 6.1.0.0. As far as I know you cannot use Find-Module to fetch the download url so we need to query the Gallery ourselves.
$moduleInfo = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/Packages?`$filter=Id eq 'ComputerManagementDsc' and Version eq '6.1.0.0'"
$moduleInfo.content.src
We get the following link: https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/package/ComputerManagementDsc/6.1.0. The link is not a direct link to the package artifact itself but it is good enough for the resource. By using this link, we let the PowerShell Gallery be responsible for providing the resource with the correct link. This is good as the storage locations might change over time.
Let’s update the Terraform file with the resource (in the end of the post, I’ll have a complete example).
resource "azurerm_automation_module" "computermanagementdsc" {
name = "ComputerManagementDsc"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
module_link = {
uri = "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/package/ComputerManagementDsc/6.1.0"
}
}
Now we need the configuration to be compiled and we are going to read it using the Terraform file function. First let’s compile it (Note that I’m compiling it in directory where the Terraform file is located, resulting in a sub-directory called timezone and containing a file called localhost.mof).
configuration timezone {
Import-DscResource -ModuleName ComputerManagementDsc -ModuleVersion 6.1.0.0
TimeZone westeustandard {
IsSingleInstance = 'Yes'
TimeZone = 'W. Europe Standard Time'
}
}
timezone
I’m compiling my DSC Configuration using PowerShell 6.1.2 resulting in an UTF-8 encoded mof file. When running this on PowerShell 5.1 you’ll end up with a UTF-16 LE encoded file which needs to be converted to UTF-8 for the Terraform file function to be able to read the file.
Now we need to add 2 resources to the Terraform file:
- azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration
- azurerm_automation_dsc_nodeconfiguration
The reason we need both is that no mof file can be uploaded to Azure Automation without a corresponding configuration to be already present for it (even an empty one). This need is abstracted away from you when you use the Azure portal or other tooling but when dealing with the REST api directly you’ll quickly find it out).
Let’s add the resources:
resource "azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration" "timezone" {
name = "timezone"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
location = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.location}"
content_embedded = "configuration timezone {}"
}
resource "azurerm_automation_dsc_nodeconfiguration" "timezone" {
name = "timezone.localhost"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
depends_on = ["azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration.timezone"]
content_embedded = "${file("${path.cwd}/timezone/localhost.mof")}"
}
Note the explicit
depends_onat the azurerm_automation_dsc_nodeconfiguration. This is because terraform will not see the dependency itself.
The Terraform file is now complete, let’s see it in full, plan and apply.
variable "ARM_CLIENT_ID" {}
variable "ARM_CLIENT_SECRET" {}
variable "ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID" {}
variable "ARM_TENANT_ID" {}
provider "azurerm" {
version = "1.21"
client_id = "${var.ARM_CLIENT_ID}"
client_secret = "${var.ARM_CLIENT_SECRET}"
subscription_id = "${var.ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}"
tenant_id = "${var.ARM_TENANT_ID}"
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "aadscrg" {
name = "aadscrg"
location = "westeurope"
}
resource "azurerm_automation_account" "aa" {
name = "aadsc01"
location = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
sku {
name = "Basic"
}
}
resource "azurerm_automation_module" "computermanagementdsc" {
name = "ComputerManagementDsc"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
module_link = {
uri = "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/package/ComputerManagementDsc/6.1.0"
}
}
resource "azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration" "timezone" {
name = "timezone"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
location = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.location}"
content_embedded = "configuration timezone {}"
}
resource "azurerm_automation_dsc_nodeconfiguration" "timezone" {
name = "timezone.localhost"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.aadscrg.name}"
automation_account_name = "${azurerm_automation_account.aa.name}"
depends_on = ["azurerm_automation_dsc_configuration.timezone"]
content_embedded = "${file("${path.cwd}/timezone/localhost.mof")}"
}
First we run terraform init (note that the environment variables for the azurerm provider are already set):
Now we can run terraform plan:
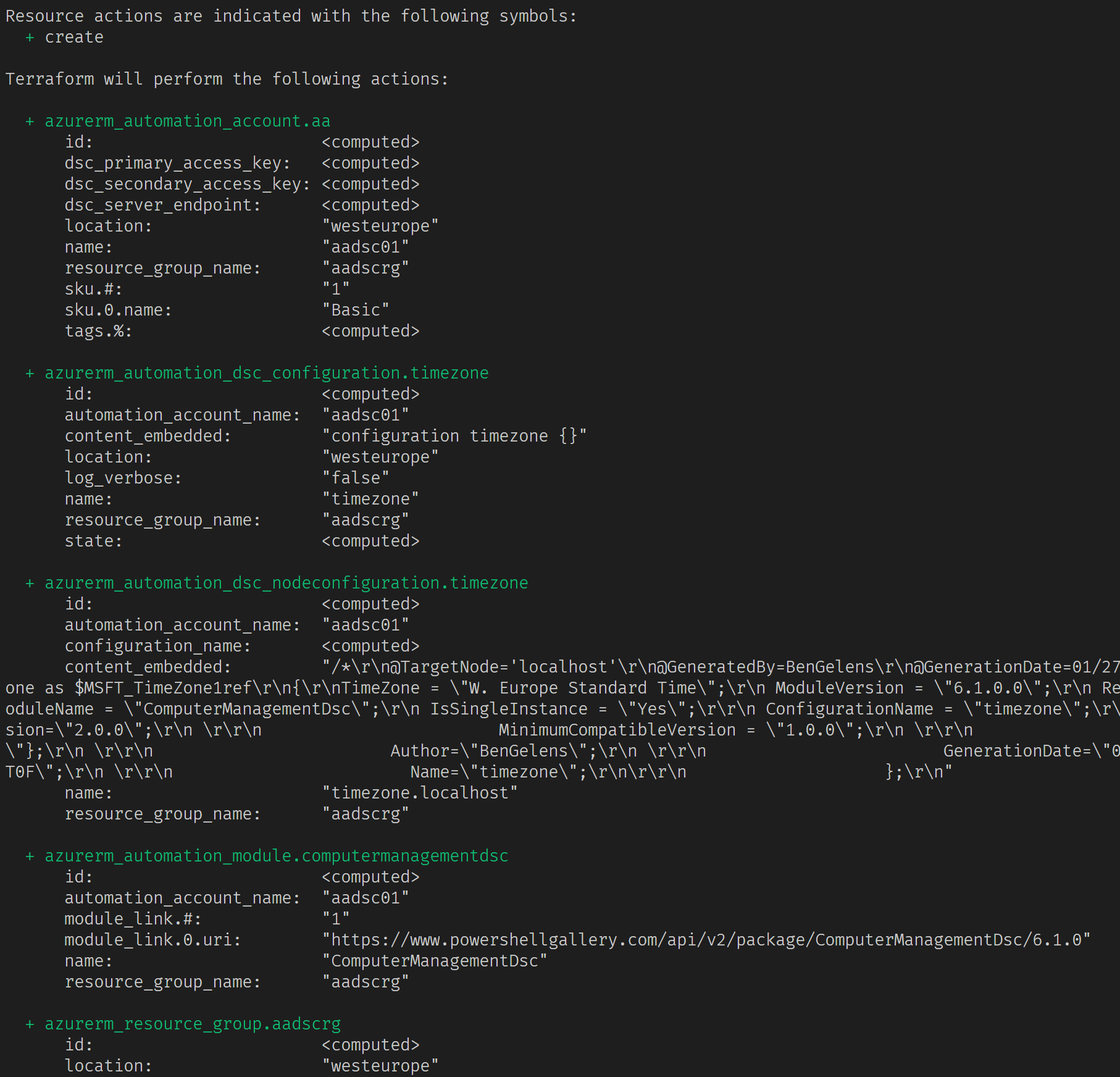
We see the resources that will be created when we would run a terraform apply. Let’s do that:
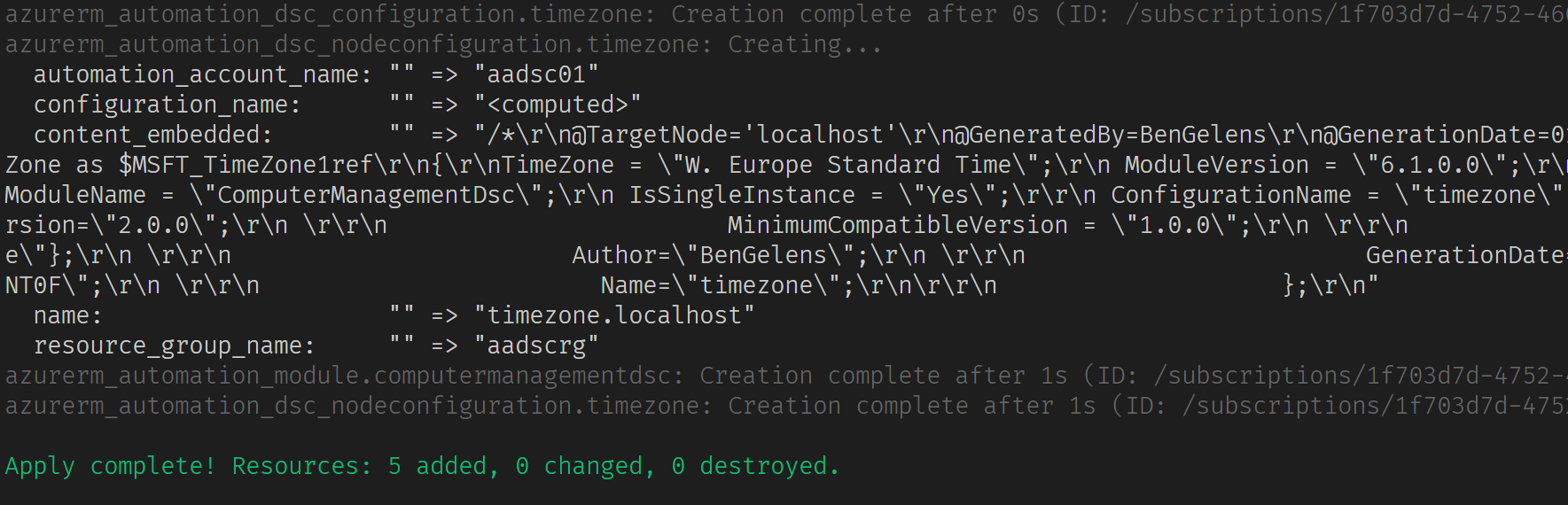
Everything is now in place for a VM to onboard and have this configuration assigned!
